By Mahmudul Hasan, Deputy Manager, Project Management (Muspana)
Climate change is no longer a distant concern. It is a global reality shaping how nations produce energy, design infrastructure, and plan for the future. Since the 1800s, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have been the primary driver of climate change. The release of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane has caused long-term shifts in temperature and weather patterns, leading to droughts, floods, rising sea levels, catastrophic storms, and declining biodiversity
To prevent the most severe impacts, scientists worldwide agree that global temperature rise must be limited to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. This consensus led to global frameworks such as the Sustainable Development Goals, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, and most importantly, the Paris Agreement (COP21). Under this agreement, countries committed to reducing emissions through Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) by cutting fossil fuel use and accelerating renewable energy deployment.
Why Solar PV Is Central to Emission Reduction
Among renewable technologies, solar photovoltaic (PV) power stands out as one of the most scalable, versatile, and globally applicable solutions. Solar PV directly converts sunlight into electricity without emissions, water consumption, or fuel dependency. As countries look to decarbonize their energy sectors, PV has become a cornerstone technology for emission reduction, energy security, and sustainable growth.

Global PV Market: Strong Growth Momentum
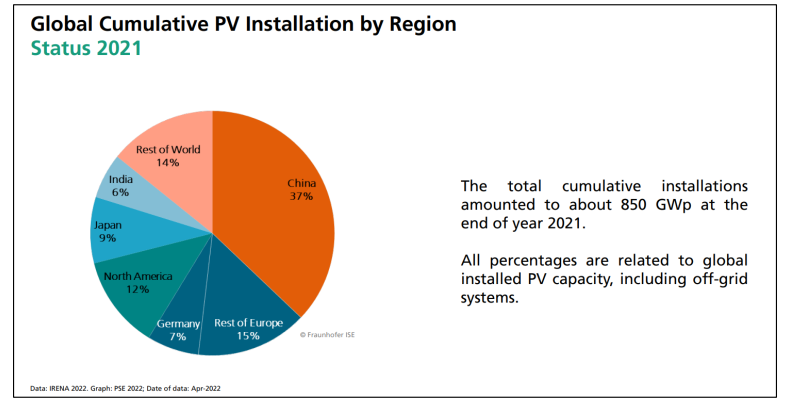
The global PV market has experienced continuous and accelerating growth. Cumulative installed capacity has risen sharply year after year, with annual new installations exceeding 100 GWp in recent years. This sustained expansion reflects falling module prices, improved efficiencies, and strong policy support across regions.
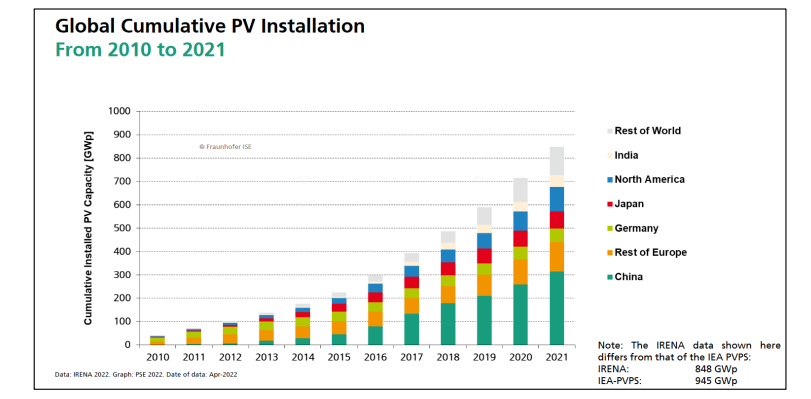
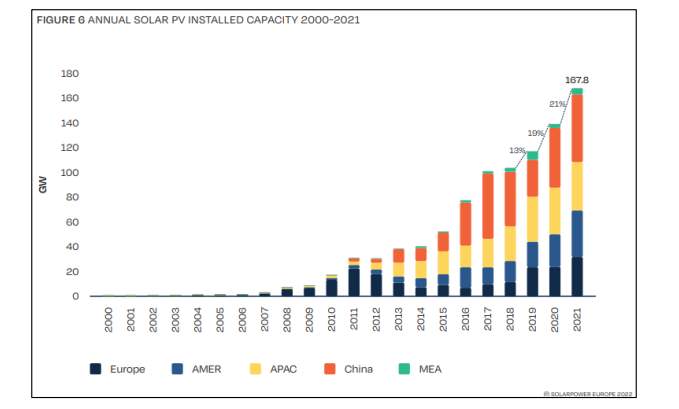
China currently leads the world in total installed PV capacity, driving both manufacturing scale and deployment.
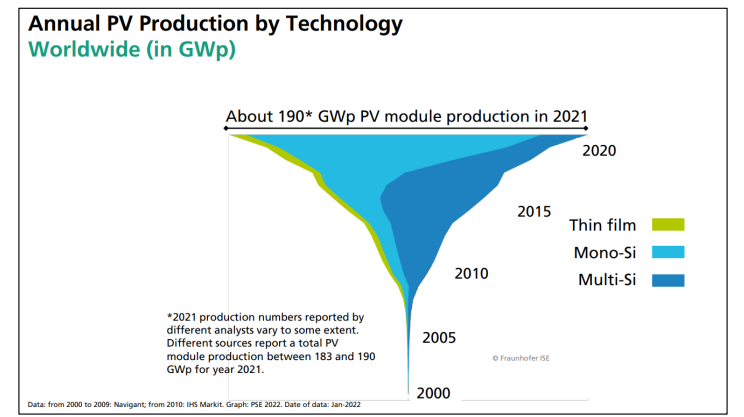
At the technology level, monocrystalline silicon cells now dominate the market, replacing older polycrystalline technologies due to their higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and better performance under real-world conditions.
PV in Bangladesh: A Natural Advantage
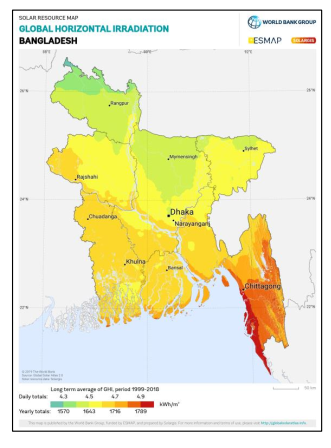
Bangladesh is exceptionally well-positioned to benefit from solar PV. The country receives strong solar irradiation, with Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) reaching up to 1,800 kWh/m² in regions such as Chattogram, and national averages around 1,600 kWh/m². These conditions support high specific yields of approximately 1,500 kWh/kWp, making solar PV technically and economically viable across the country.
At the same time, Bangladesh faces rising electricity demand, grid pressure, and land scarcity. These realities make rooftop PV systems especially important. As the relevance of PV increases, so does the demand for high-quality systems, reliable components, and professional installation standards.
Looking Ahead
The global PV market is not just growing; it is reshaping how energy systems are built. For countries like Bangladesh, solar PV represents a pathway to cleaner power, energy independence, and climate resilience. With proper planning, quality-focused deployment, and continued innovation, PV will remain one of the most powerful tools in the global transition toward sustainable energy.