By Md. Hasan Habib, System Engineer (Muspana)
Street lighting is no longer just about turning lights ON at sunset and OFF at sunrise. In today’s cities, lighting has evolved into an intelligent infrastructure that responds to its surroundings, optimizes energy use, and reports its own performance. This transformation is known as smart lighting.
At Muspana, we view smart lighting not as a single product, but as a complete system that makes every light point aware, responsive, and measurable.
What Is Smart Lighting?
Smart lighting is a connected lighting system where each luminaire can:
-
Adjust brightness based on time, movement, or ambient light
-
Detect faults and report its health status
-
Communicate with a central control platform
-
Reduce energy consumption without compromising safety
These systems are widely used in street lighting, industrial zones, campuses, and large outdoor areas, where operational efficiency and reliability are critical.
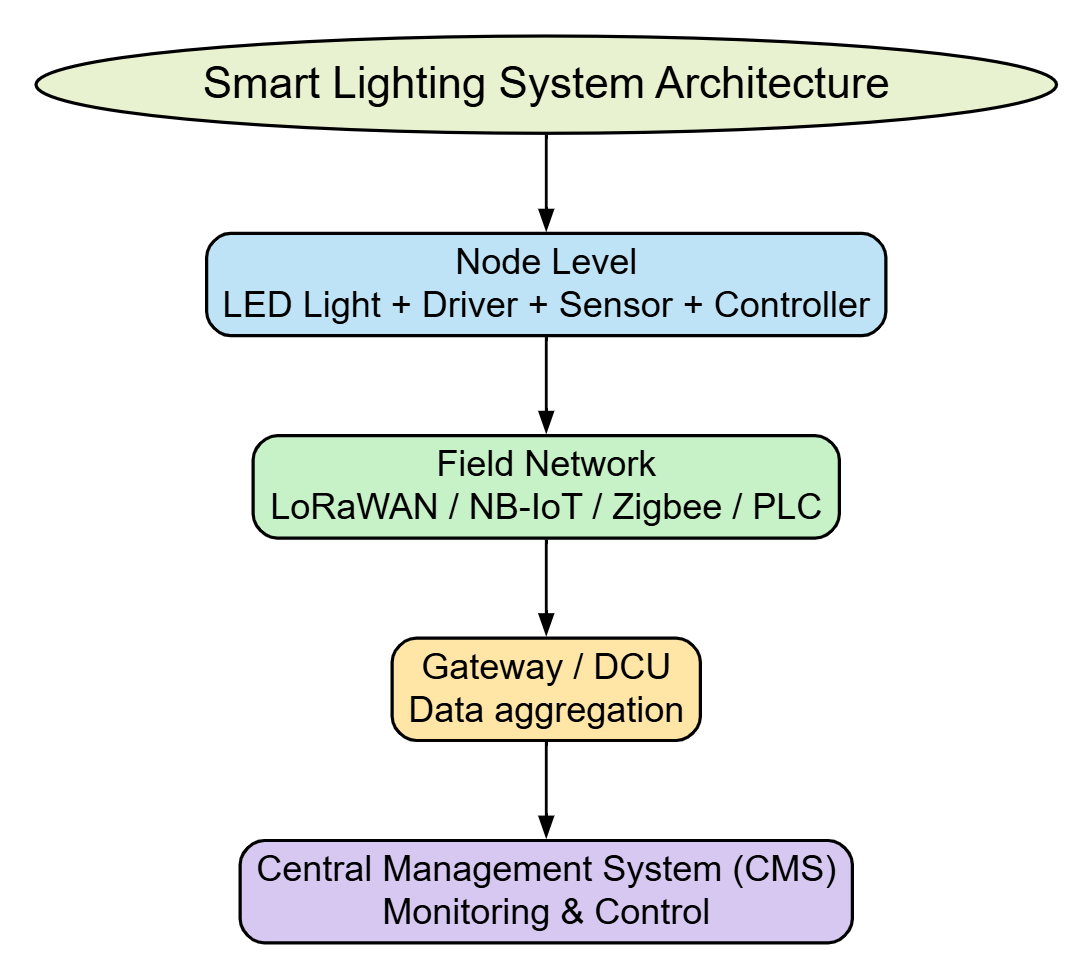
The 4-Layer Architecture of Smart Lighting
The easiest way to understand smart lighting is through its layered design.
1. Node Level (At the Pole)
This is where intelligence begins. Each street light contains an LED driver, sensors, a controller, and a communication module. Local decisions such as dimming, switching, and basic fault detection happen right at the pole.
2. Field Network
Individual lights communicate with each other and with gateways using technologies like LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, Zigbee, or Power Line Communication (PLC). This network allows commands to be sent and performance data to be collected.
3. Gateway Layer
Gateways or Data Concentrator Units collect data from multiple poles and securely transmit it to the server or cloud. They make large-scale lighting systems manageable.
4. Central Management System (CMS)
The CMS is the control room. Operators can monitor live status, create dimming schedules, receive fault alerts, and analyze energy consumption through dashboards and maps.
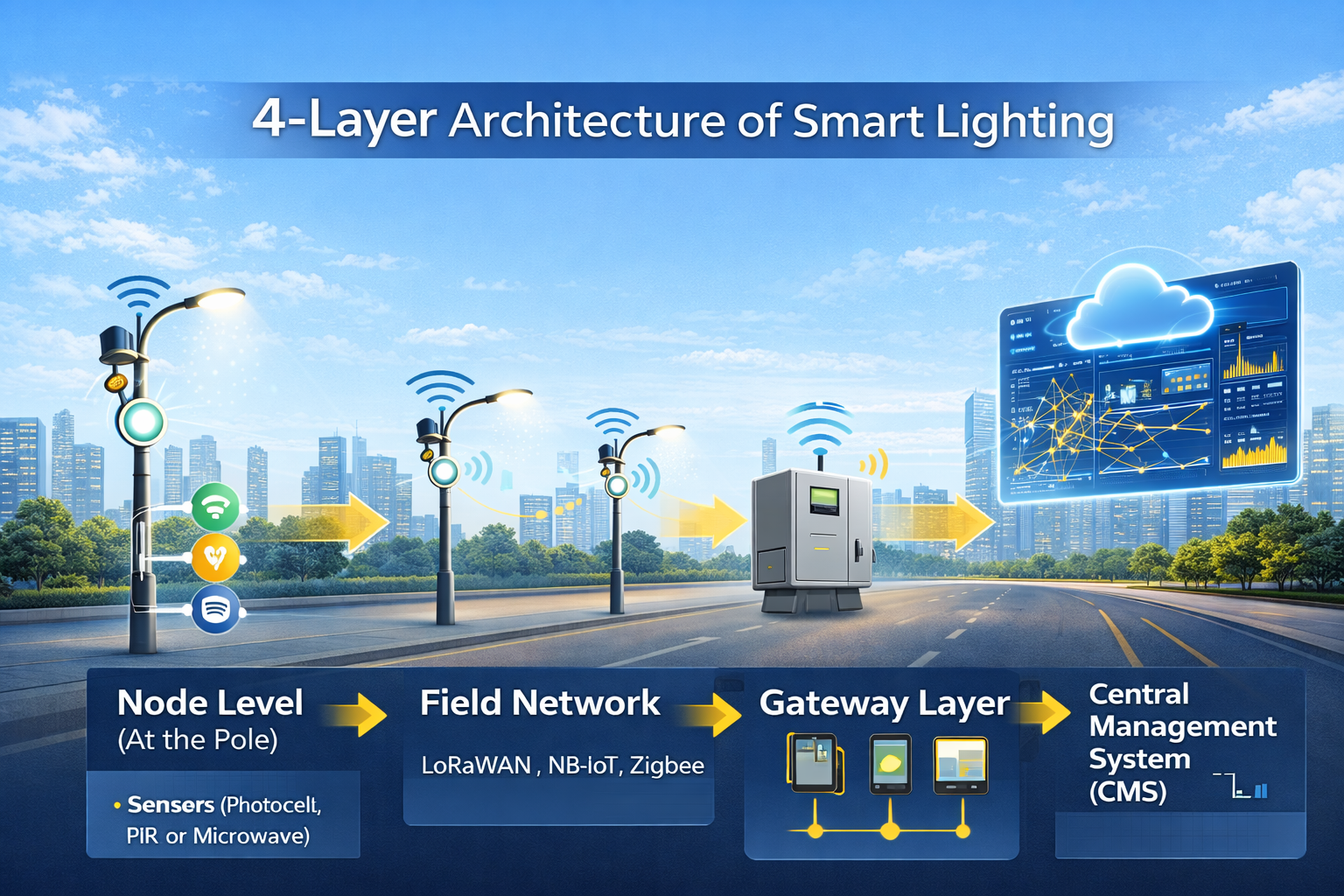
Even if communication fails, smart lights continue operating using the last known schedule, ensuring reliability at all times.
Key Components of a Smart Lighting System
A smart lighting system works because each component has a defined role:
-
Smart LED drivers for precise power control
-
Standardized interfaces like NEMA or Zhaga sockets
-
Sensors such as photocells, PIR, or microwave sensors
-
Street light controllers acting as the local brain
-
Surge protection devices (SPD) to protect electronics
-
Gateways and CMS software for centralized control
Together, these components turn lighting infrastructure into a managed digital asset.
Why Cities Are Adopting Smart Lighting
Smart lighting delivers measurable benefits:
-
50–70% energy savings through adaptive dimming
-
Faster maintenance due to automatic fault alerts
-
Lower operational costs and fewer site visits
-
Improved road safety and public comfort
-
Reduced carbon emissions
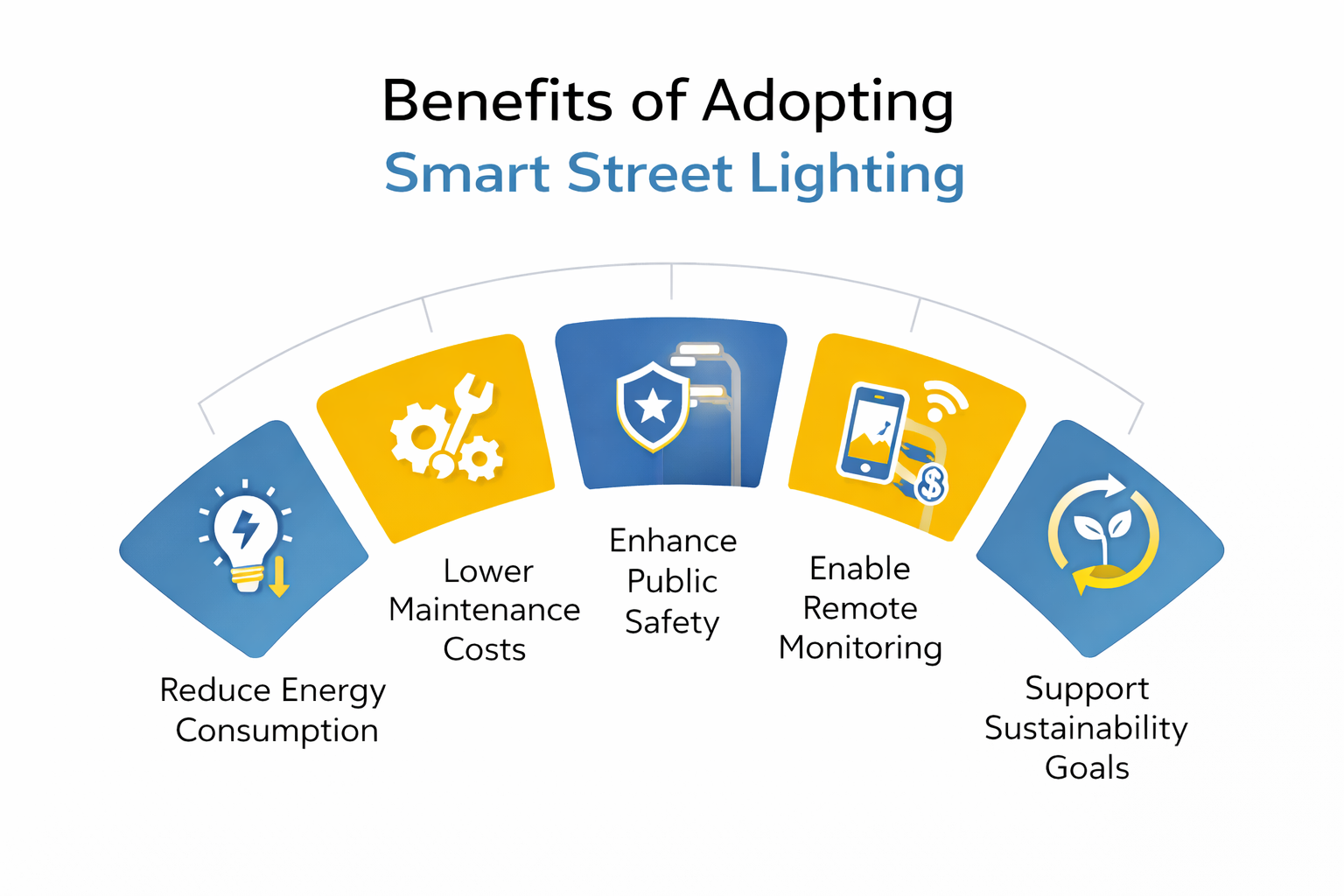
For municipalities and organizations, smart lighting is one of the fastest-return investments in urban infrastructure.
Smart Lighting with Muspana
At Muspana, we design and deploy smart lighting systems tailored to local conditions, traffic patterns, and operational goals. Our approach combines robust hardware, secure communication, and intelligent software to deliver reliable, future-ready lighting solutions.
Smart lighting is not just about illumination. It is about creating safer streets, efficient cities, and infrastructure that thinks ahead.




