By Md. Nur Nabi, Sr. Engineer (Muspana)
When we look at a city skyline, we often notice the roads, buildings, and lights. What usually goes unnoticed are the tall vertical structures quietly holding everything together. Poles are among the most essential yet underestimated components of modern infrastructure. From powering cities to enabling communication and ensuring public safety, poles form the backbone of urban, industrial, and transportation systems.
At its core, a pole is a vertical structural member designed to support overhead loads such as electrical cables, lighting fixtures, communication equipment, traffic signals, and signage. Though slender in appearance, a properly engineered pole is built to withstand heavy loads, harsh weather, and long-term environmental stress while maintaining stability and safety.
What Makes a Pole Reliable?
A well-designed pole is defined by more than its height. Structural strength is critical, allowing the pole to resist vertical and lateral forces caused by wind, vibration, cables, and mounted equipment. Material durability also plays a vital role. Poles are commonly manufactured from reinforced concrete, galvanized steel, aluminum, or treated timber, each selected based on corrosion resistance, lifespan, and application environment.
Equally important is the foundation system. A strong embedded or foundation base ensures that loads are safely transferred to the ground, preventing tilting or failure. Safety features such as proper earthing, insulation clearance, and anti-corrosion coatings help protect both people and equipment. Modern poles are also designed with attachment provisions, including brackets, arms, and mounting points, allowing flexible installation of lights, cables, cameras, antennas, or signage.
In urban areas, aesthetics matter too. Decorative finishes and elegant designs help poles blend seamlessly into city landscapes without compromising performance.
Different Types of Poles and Their Uses
Poles are classified based on their function.
Electrical poles support power transmission and distribution networks, ranging from low tension to extra high voltage lines. 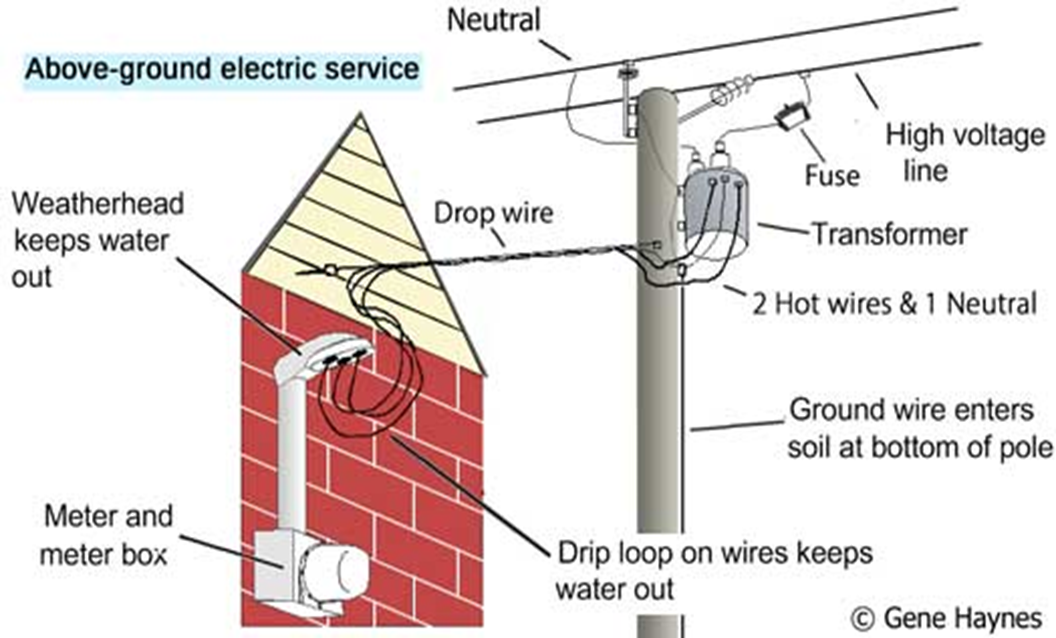
Street light poles illuminate roads, parks, and public spaces, and include single-arm, double-arm, high-mast, and decorative designs.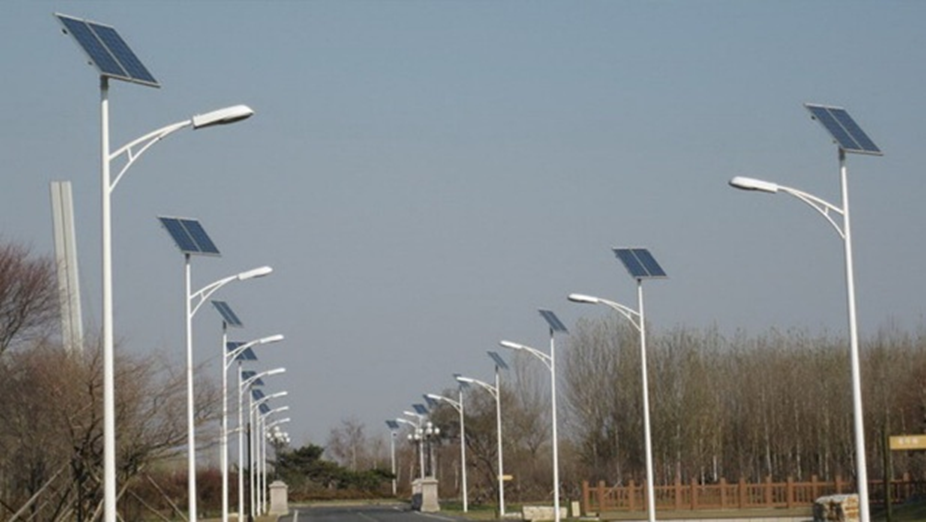
Communication poles carry telecom cables, fiber optics, antennas, and CCTV systems, enabling uninterrupted connectivity.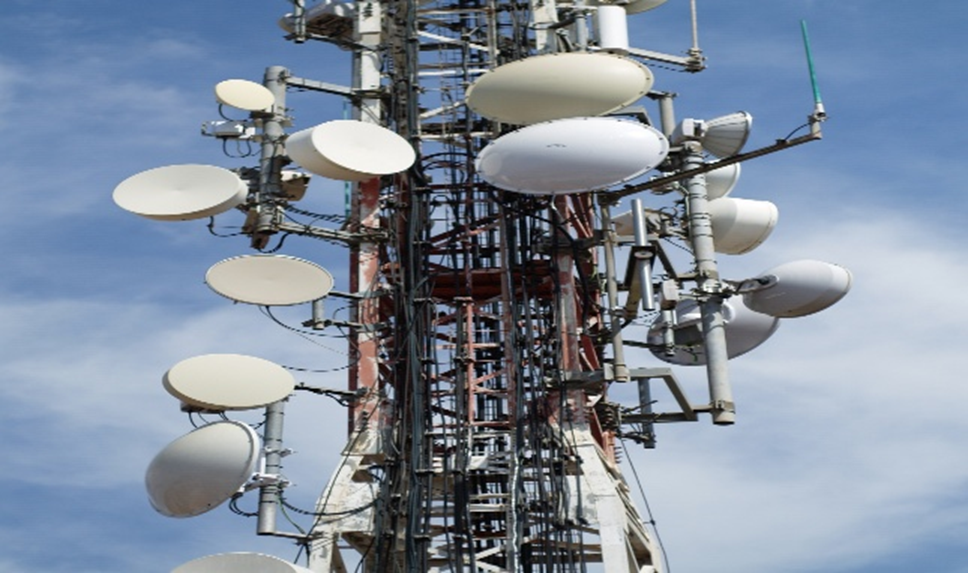
Traffic signal poles play a crucial role at intersections and highways by supporting signals, cameras, and road signs.
Utility poles combine electrical and communication lines on a single structure to optimize space and cost.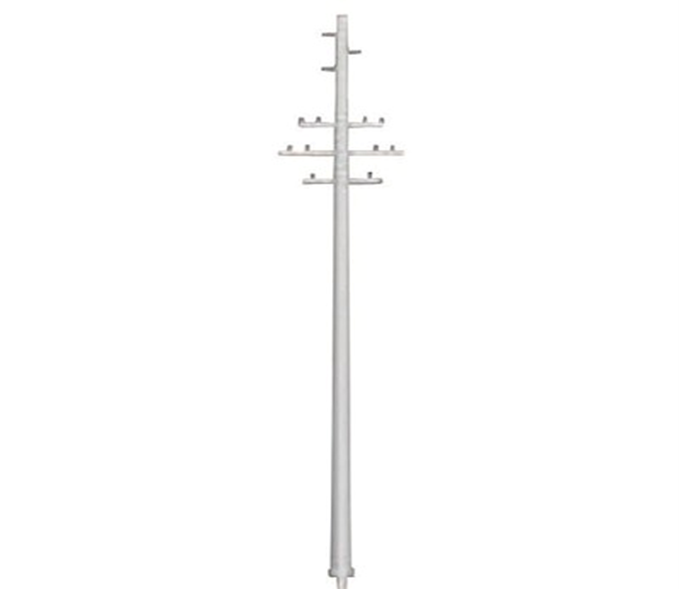
For large open areas like highways, ports, stadiums, and industrial yards, high mast poles provide wide-area lighting.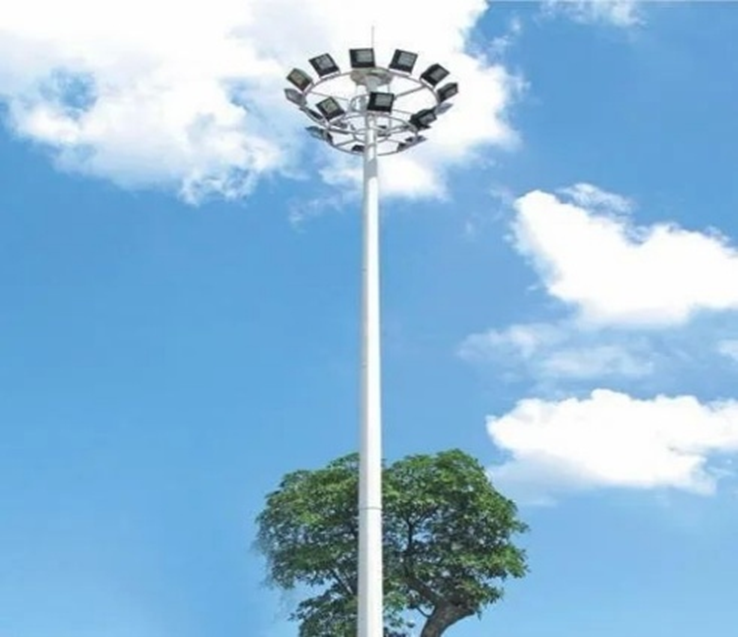
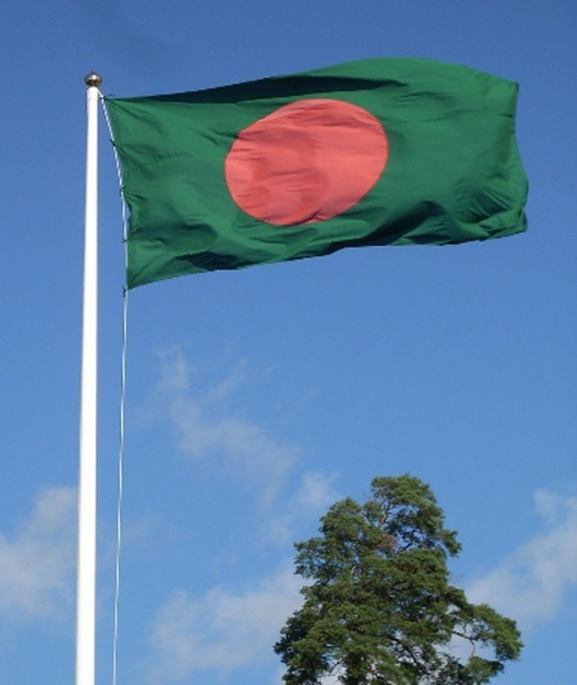
There are also flag poles that are used for displaying national or institutional flags, commonly installed in government, buildings, schools, and public spaces.

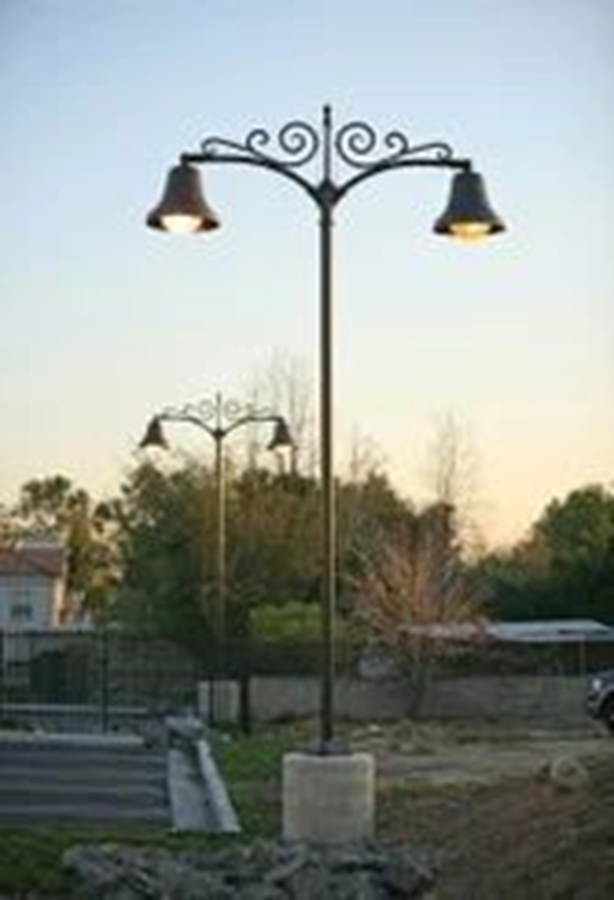
Also there are decorative architectural poles, which add identity and visual appeal to public and institutional spaces.

Building Smarter Cities with the Right Poles
As cities expand and infrastructure becomes smarter, the demand for reliable, durable, and well-designed poles continues to grow. Whether it is lighting streets, transmitting power, supporting communication, or enhancing urban aesthetics, poles quietly enable the systems we depend on every day.
At Muspana, we understand that choosing the right pole is not just a structural decision. It is an investment in safety, longevity, and the future of sustainable infrastructure.